Ever wonder how your salary progresses as a federal employee under the General Schedule (GS) pay system? The key lies in understanding GS step increases, governed by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM). These incremental raises are crucial to your overall compensation and long-term financial planning. Let's explore this essential aspect of federal employment.
A GS step increase is a periodic pay raise within a specific GS grade. These raises generally occur based on satisfactory job performance and time in service. OPM regulations dictate the frequency and amount of these increases. Understanding these guidelines is vital for predicting your future earnings and making informed career decisions.
The GS step increase system has a rich history tied to the development of the General Schedule itself. Created to standardize federal pay and promote fair compensation, the step increase component aims to reward consistent performance and longevity. It provides a transparent path for salary growth, encouraging employee retention and fostering a stable workforce.
The importance of GS step increases extends beyond individual financial gain. They contribute to a well-structured and predictable compensation system within the federal government, fostering fairness and transparency. This system plays a vital role in attracting and retaining qualified employees, ensuring the government has a skilled and dedicated workforce.
However, sometimes issues can arise related to step increases. For example, delays in processing step increases can occur, or there may be confusion surrounding eligibility criteria. Understanding the regulations and your rights as a federal employee is crucial in addressing these potential challenges. Resources like the OPM website and your agency's HR department can offer support and guidance.
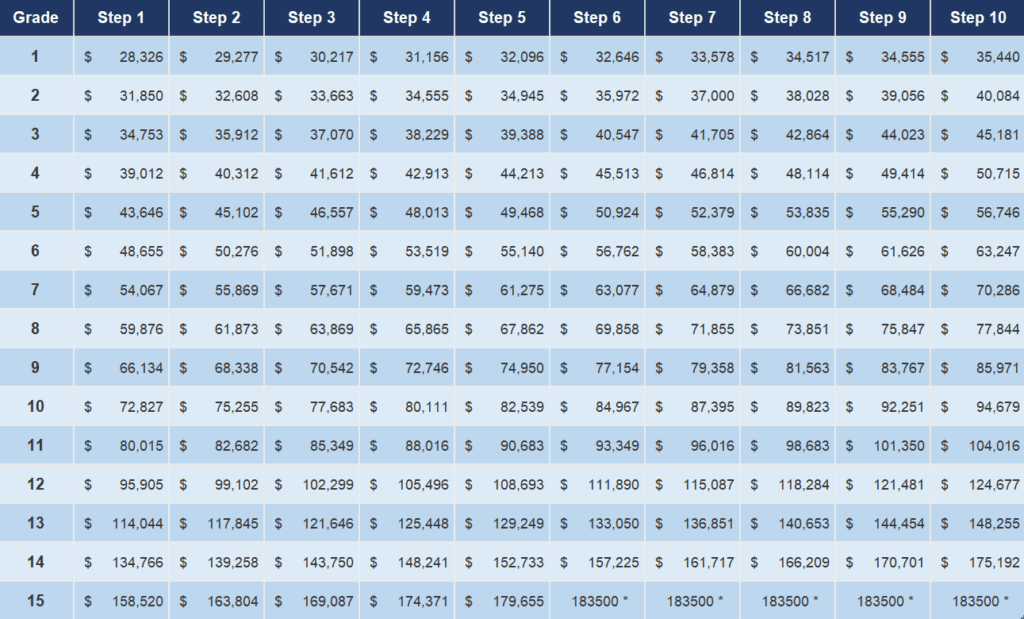
A GS step increase is a set percentage increase to your base salary within your current grade. For example, a GS-7, Step 1 employee might move to GS-7, Step 2 after a specified period, receiving a predetermined raise. The amount of the increase depends on the GS grade and step level.
Three key benefits of GS step increases include: Predictable Salary Growth, Motivation for Performance, and Enhanced Retention.
Predictable Salary Growth: The structured nature of step increases allows employees to anticipate future earnings, facilitating better financial planning. For instance, knowing your step increase schedule can help you budget for long-term goals like buying a house or investing in retirement.
Motivation for Performance: Step increases tied to satisfactory performance encourage employees to maintain high work standards. This incentive promotes a culture of excellence and productivity within the federal workforce.
Enhanced Retention: Regular salary growth through step increases helps retain valuable employees, reducing turnover costs for the government and fostering stability within agencies. Employees are more likely to stay with an organization that offers a clear path for career progression and consistent compensation improvements.
To understand your step increase eligibility, consult your agency's HR department and the OPM website. They can provide specific information about waiting periods and performance requirements for your GS grade and position.
Advantages and Disadvantages of GS Step Increases
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable Salary Growth | Potentially Slower Growth Than in Private Sector |
| Motivates Consistent Performance | Can Be Affected by Budgetary Constraints |
| Enhances Employee Retention | Limited Flexibility in Salary Adjustments |
For further information, consult the OPM website (www.opm.gov).
Five best practices related to GS step increases: understand OPM regulations, track your progress, maintain satisfactory performance, address any discrepancies promptly, and plan your career trajectory.
While the GS step increase system is designed to provide a fair and transparent path for salary growth, it's essential to understand its limitations and prepare for potential challenges. Budgetary constraints or changes in government regulations can sometimes impact the timing or amount of step increases. Staying informed and proactive is key to navigating these complexities and maximizing your career progression within the federal government.
Frequently Asked Questions: What is a GS step increase? How often do they occur? How is the amount determined? What happens if my step increase is delayed? Where can I find more information about my specific step increase eligibility? Who do I contact if I have questions about my step increase? Can my step increase be denied? What is the within-grade increase (WGI) waiting period?
Tips for navigating the GS step increase system: stay informed about OPM regulations, communicate with your supervisor, document your performance, and understand your agency's internal procedures.
In conclusion, understanding the mechanics of GS step increases is crucial for every federal employee under the General Schedule. This system provides a structured path for salary growth, rewarding consistent performance and longevity. By familiarizing yourself with OPM regulations, staying proactive, and planning strategically, you can effectively leverage the GS step increase system to maximize your earnings potential and achieve your long-term career goals within the federal government. This not only benefits your personal finances but also contributes to a stable and motivated federal workforce. Take ownership of your career progression by understanding and utilizing the resources available to you. Remember, informed employees are empowered employees.
Opm Gs Pay Scale 2024 Increase - The Brass Coq
Gs Pay Scale 2024 Increase Opm - The Brass Coq
Opm Gs Pay Scale 2024 With Locality - The Brass Coq
Gs Pay Scale 2024 Opm Increase - The Brass Coq
2024 Gs Pay Scale Increase Notification Pdf - The Brass Coq
gs step increase opm - The Brass Coq
Gs Pay Scale 2024 Increase With Locality Pay - The Brass Coq