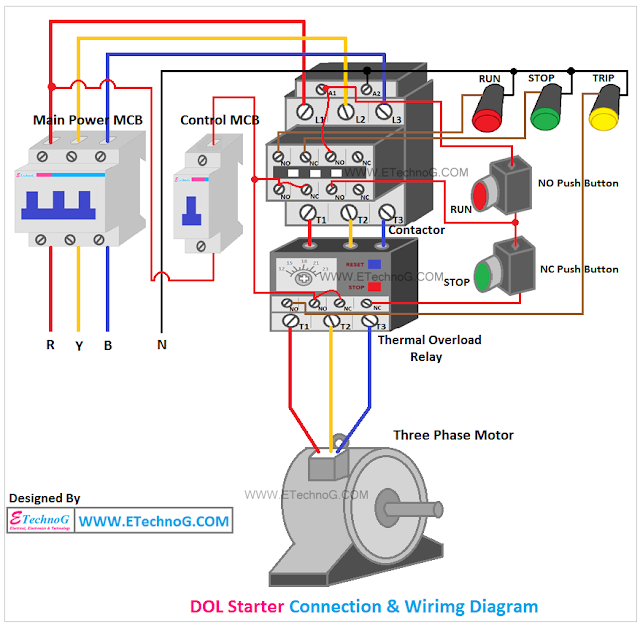
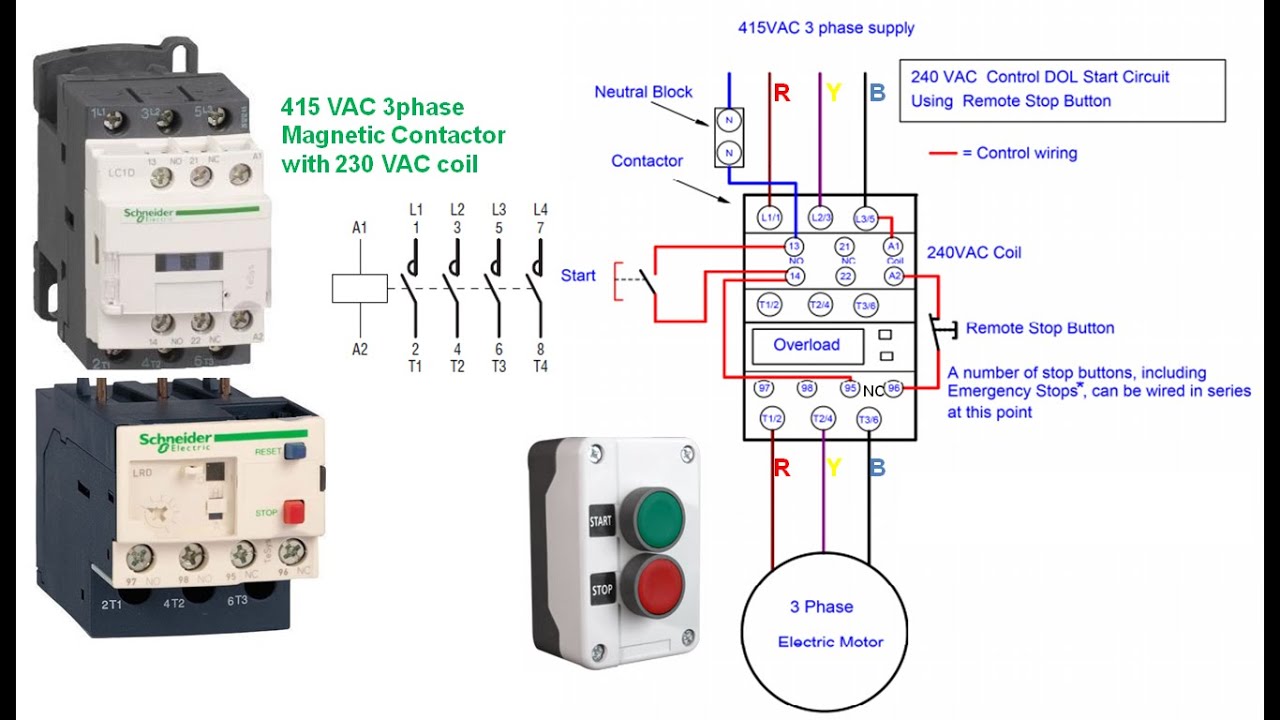
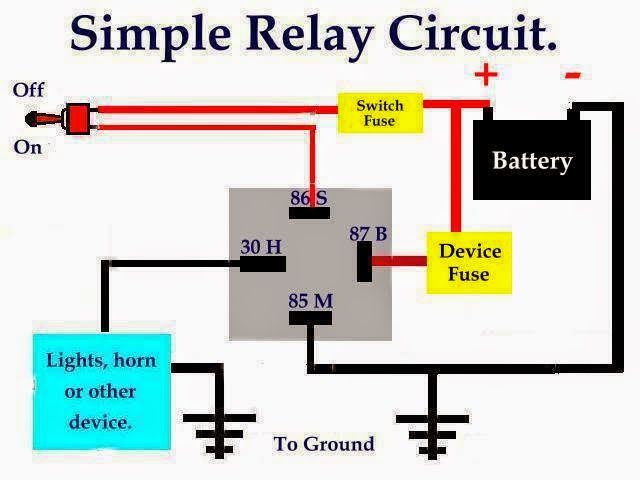
Ever wondered how a small key can crank a powerful engine to life? The secret often lies within a seemingly simple device: the starter relay control circuit. This unassuming component plays a crucial role in managing the high current needed to start an engine, protecting the ignition switch and other components from damage.
A starter relay control circuit acts as an intermediary between the ignition switch and the starter motor. When you turn the key, a small current flows through the ignition switch and activates the relay. This, in turn, closes a high-current circuit, allowing power to flow to the starter motor and crank the engine. Think of it as an electrical amplifier, using a small signal to control a much larger one.
Without a starter relay, the ignition switch would have to handle the full current required by the starter motor, leading to premature wear and potential failure. The starter relay's function is therefore critical for the reliable operation of any vehicle or machine equipped with an electric starter. It's a simple yet elegant solution to a complex electrical challenge.
The principles behind starter relay control have been around for decades, evolving alongside automotive technology. Early systems were simpler, but modern circuits incorporate additional features for safety and efficiency. Understanding how these circuits work can be invaluable for anyone working with engines, from mechanics to hobbyists.
One common issue related to starter control systems is a malfunctioning relay. This can prevent the engine from starting, leaving you stranded. Learning to diagnose and troubleshoot these circuits is a valuable skill. By understanding the basic components and their interactions, you can quickly identify and resolve problems.
A starter relay typically consists of an electromagnetic coil, a movable armature, and a set of contacts. When the coil is energized, it creates a magnetic field that pulls the armature, closing the contacts and completing the circuit to the starter motor. The circuit's simplicity contributes to its robustness and reliability.
One key benefit of using a starter relay circuit is increased safety. By isolating the high-current circuit from the ignition switch, it reduces the risk of fire and electrical damage. Another advantage is improved reliability. The relay protects the ignition switch from excessive current, extending its lifespan.
A third benefit is the ability to integrate additional features, such as anti-theft systems and remote starting capabilities. Modern starter relay control circuits can be designed to incorporate these functionalities, enhancing security and convenience.
If you suspect a faulty starter relay, a simple test involves using a jumper wire to bypass the relay. If the engine starts with the relay bypassed, the relay is likely the culprit. Replacement is typically straightforward and inexpensive.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Starter Relay Control Circuits
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Potential Relay Failure |
| Improved Reliability | Added Complexity (compared to direct switching) |
| Integration of Additional Features |
Best Practices for Implementing Starter Relay Control Circuits:
1. Use the correct gauge wiring for the high-current circuit.
2. Ensure secure connections to prevent voltage drops.
3. Choose a relay with an appropriate current rating.
4. Protect the circuit with a fuse or circuit breaker.
5. Regularly inspect the relay for signs of wear or damage.
Real-World Examples: Automobiles, Motorcycles, Boats, Lawn Mowers, Generators.
Challenges and Solutions: Corrosion on terminals can be cleaned with a wire brush. A faulty relay can be replaced with a new one. A blown fuse indicates a short circuit, which needs to be diagnosed and repaired.
FAQ: What is a starter relay? How does it work? Why is it important? What are the signs of a bad starter relay? How do I test a starter relay? How do I replace a starter relay? What type of relay do I need for my application?
Tips and Tricks: Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical system. Use a wiring diagram to understand the circuit layout. Use dielectric grease on connections to prevent corrosion.
The starter relay control circuit, a seemingly small component, plays a pivotal role in starting engines and powering various machines. Its ability to manage high currents safely and reliably makes it an essential part of modern electrical systems. From ensuring the smooth start of your car to powering essential equipment, understanding the function and maintenance of this circuit can empower you to maintain and troubleshoot effectively. By understanding the benefits, applications, and best practices outlined in this article, you can appreciate the elegant simplicity and undeniable importance of the starter relay control circuit. Take the time to familiarize yourself with this critical component – it’s an investment in both knowledge and peace of mind.
Reversing Motor Starter Wiring - The Brass Coq
Dol Starter Circuit Diagram Single Phase - The Brass Coq
SOLVED P0616 Code Low Voltage Starter Relay Control Circuit - The Brass Coq
1990 ford f150 starter relay wiring diagram Wiring Core - The Brass Coq
starter relay control circuit - The Brass Coq
Remote Starter Wiring Diagrams Automotive - The Brass Coq
starter relay control circuit - The Brass Coq
Relay Control Circuit Diagram - The Brass Coq
starter relay control circuit - The Brass Coq
P2510 Code ECMPCM Power Relay Sense Circuit RangePerformance - The Brass Coq
1992 Chevrolet Truck Starter Wiring - The Brass Coq
starter relay control circuit - The Brass Coq
starter relay control circuit - The Brass Coq
Jeep Power Control Module QA - The Brass Coq
P0615 Mercedes Starter Relay Control Circuit - The Brass Coq