Ever feel like the world is getting a little too warm? You're not alone. A significant contributor to this warming trend are greenhouse gases, and understanding what they are is the first step towards mitigating their impact. So, what are greenhouse gases (or, as some might ask, "apa itu gas rumah hijau" in Indonesian)?
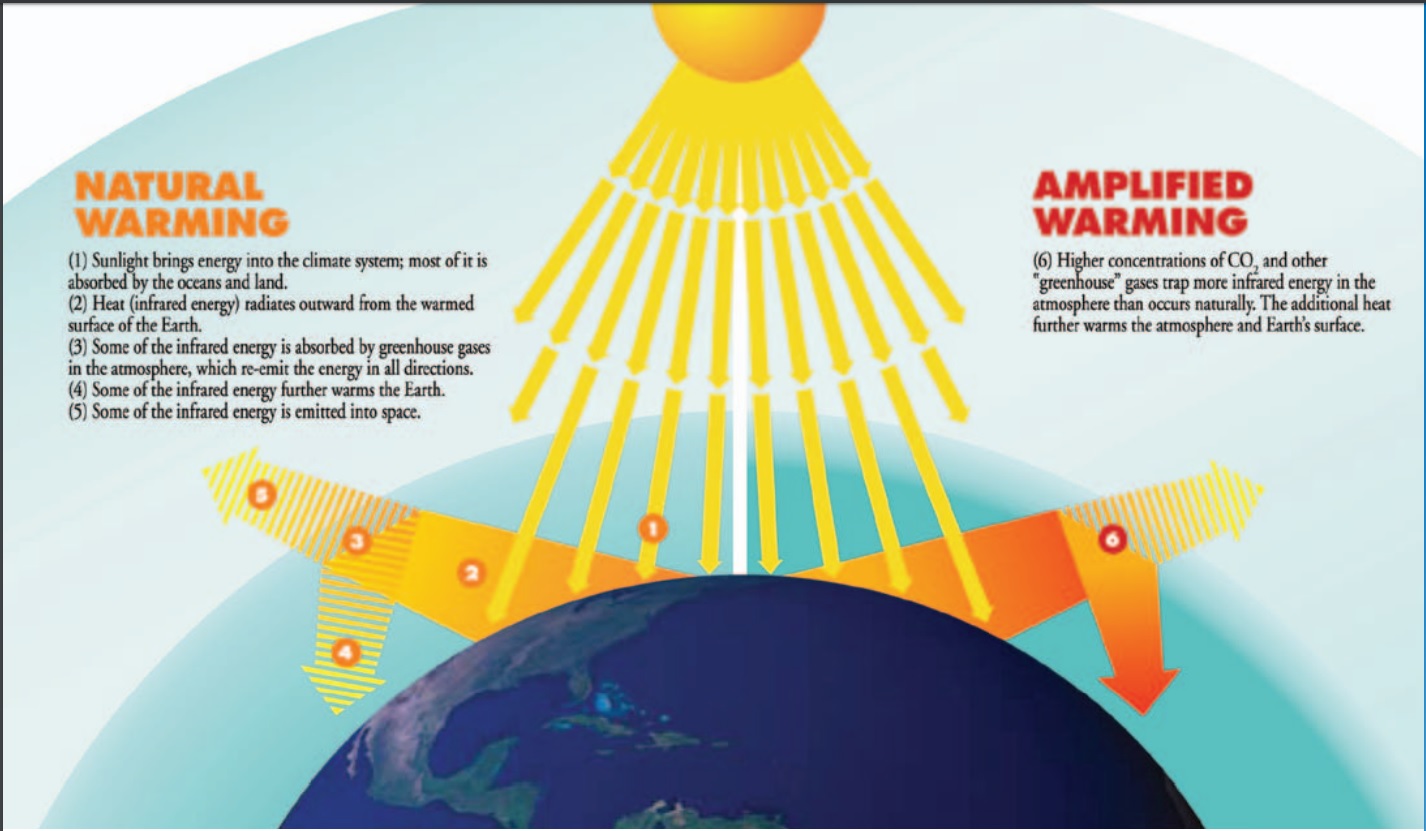
Greenhouse gases are essentially atmospheric components that trap heat. They act like a blanket around the Earth, letting sunlight in but preventing some of the heat from escaping back into space. This natural process is what makes our planet habitable, maintaining a temperature suitable for life. However, human activities have significantly increased the concentration of these gases, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming.
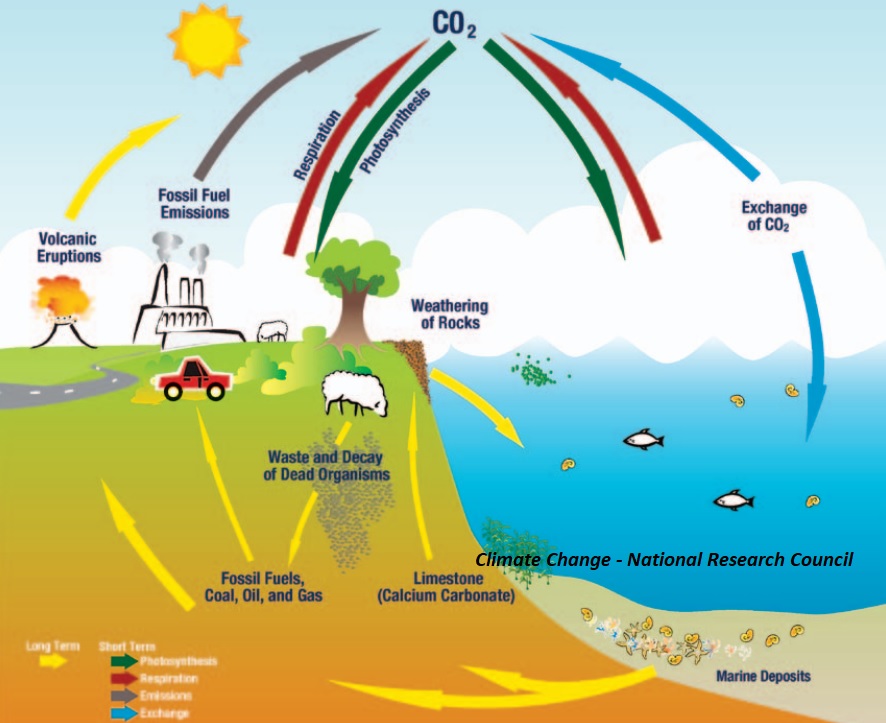
The primary greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases. These gases are released through various activities, including burning fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, agriculture, and industrial processes. The increased concentration of these gases traps more heat, leading to a rise in global temperatures and subsequent climate change.
The impact of this warming trend is widespread, affecting everything from rising sea levels and extreme weather events to disruptions in ecosystems and agricultural practices. Understanding the science behind greenhouse gases and their effects is crucial for addressing this global challenge.
So, why should you care? Because the consequences of climate change are already being felt worldwide and will continue to intensify if left unchecked. Learning about greenhouse gases empowers you to make informed choices and contribute to a more sustainable future. From reducing your carbon footprint to advocating for policy changes, every action counts.
The concept of the greenhouse effect was first proposed by Joseph Fourier in 1824 and experimentally investigated by John Tyndall in 1858, finally being quantified by Svante Arrhenius in 1896. Initially, the greenhouse effect was viewed positively as essential for life on Earth. However, the rapid industrialization of the 20th century led to a significant increase in greenhouse gas emissions, raising concerns about the potential for negative consequences. The primary issue with greenhouse gases today is not their existence, but the excessive amounts released into the atmosphere due to human activities.
For example, burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas for electricity generation releases large amounts of CO2. Similarly, deforestation removes trees that absorb CO2, further contributing to its accumulation in the atmosphere. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is released from livestock and agricultural practices. These are just a few examples of how human activities contribute to the problem.
While a certain level of greenhouse gases is essential for maintaining a habitable temperature, the excess is problematic. One benefit of the natural greenhouse effect is that it prevents extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night. Another is that it allows for liquid water to exist on Earth's surface, which is essential for all life. Lastly, it contributes to the overall stability of the Earth's climate system. However, these benefits are overshadowed by the negative impacts of excessive greenhouse gas emissions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Greenhouse Effect
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Maintains a habitable temperature on Earth | Global warming and climate change |
| Allows for liquid water to exist | Rising sea levels |
| Contributes to climate stability (within a certain range) | Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events |
Five real-world examples of the impact of greenhouse gas emissions include: rising sea levels in coastal regions, increased frequency and intensity of hurricanes, prolonged droughts in certain areas, melting glaciers and ice sheets, and changes in agricultural yields due to shifting climate patterns.
Five challenges related to greenhouse gas emissions are: transitioning to renewable energy sources, reducing emissions from agriculture and industry, promoting sustainable land use practices, fostering international cooperation on climate action, and adapting to the unavoidable impacts of climate change. Solutions include investing in renewable energy technologies, developing and implementing carbon capture technologies, promoting sustainable agriculture and forestry, enacting and enforcing environmental regulations, and educating the public about climate change and its solutions.
FAQ:
1. What is the main greenhouse gas? - Carbon Dioxide
2. What causes greenhouse gas emissions? - Primarily the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
3. What are the effects of greenhouse gases? - Global warming, climate change, rising sea levels, extreme weather events.
4. How can we reduce greenhouse gas emissions? - Transitioning to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, adopting sustainable practices.
5. What is the greenhouse effect? - The trapping of heat in the Earth's atmosphere by greenhouse gases.
6. Why are greenhouse gases important? - They regulate the Earth's temperature, making it habitable.
7. Are all greenhouse gases bad? - No, a certain level is essential for life, but excessive amounts are harmful.
8. What is the difference between the greenhouse effect and global warming? - The greenhouse effect is a natural process, while global warming is the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by human activities.
One simple tip for reducing your contribution to greenhouse gas emissions is to reduce, reuse, and recycle. By consuming less and reusing items, you reduce the demand for new products, which often involve energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Recycling helps to conserve resources and reduce waste, further minimizing your impact.
In conclusion, understanding "apa itu gas rumah hijau" or greenhouse gases is crucial in today's world. They play a vital role in regulating our planet's temperature, but excessive emissions due to human activities are driving climate change and its associated consequences. From rising sea levels to extreme weather events, the impacts are already being felt worldwide. However, by understanding the science behind greenhouse gases, we can take actionable steps to mitigate their impact. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, adopting sustainable practices, and advocating for policy changes. Every individual action, no matter how small, contributes to a collective effort towards a more sustainable and resilient future. Let's all play our part in protecting our planet for generations to come.
Emisi Gas Rumah Kaca Indonesia - The Brass Coq
Apa Itu Konsep Bangunan Hijau Di Malaysia - The Brass Coq
apa itu gas rumah hijau - The Brass Coq
Mengenal Enam Jenis Gas Rumah Kaca - The Brass Coq
Cara Menghitung Emisi Gas Rumah Kaca - The Brass Coq
Apa Itu Gas Air Mata dan Bagaimana Cara Mengatasi Paparannya - The Brass Coq
CARA FLEXI CARA CEK TAGIHAN GAS PGN - The Brass Coq
TCI MEMBANTU PENGURANGAN PELEPASAN GAS RUMAH HIJAU GHG - The Brass Coq
6 Gas Rumah Kaca Halaman all - The Brass Coq
Apa Itu Kesan Rumah Hijau - The Brass Coq
Mengenal Gas Rumah Kaca - The Brass Coq
Emisi Gas Rumah Kaca Per Provinsi - The Brass Coq
Apa Itu Pengertian Efek Rumah Kaca dan Apa Saja Dampaknya - The Brass Coq
Apa Itu Kesan Rumah Hijau - The Brass Coq
Gambar Gas Rumah Kaca - The Brass Coq