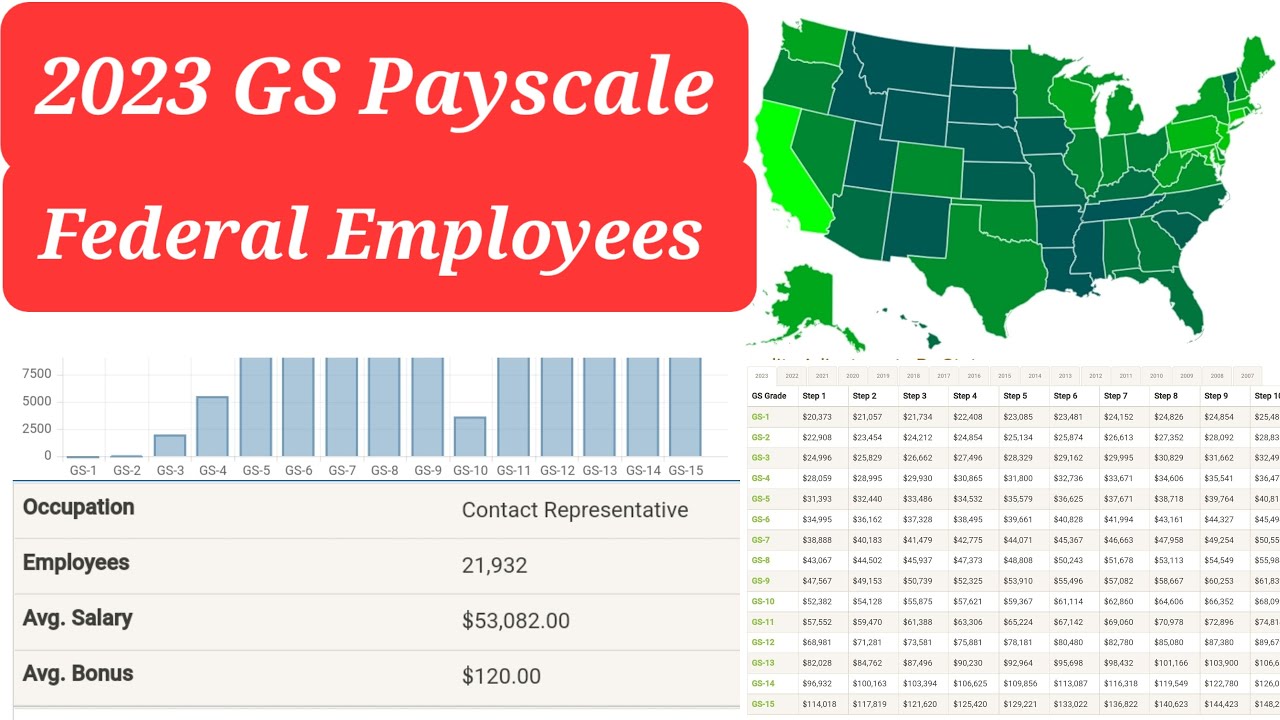
Navigating the federal government's General Schedule (GS) pay system can feel like traversing a complex landscape. For employees, understanding how pay increases work within this system is crucial for career planning and financial well-being. This comprehensive guide aims to simplify the GS pay scale and its grade increase rules, offering clarity and actionable insights.
The GS pay scale is the backbone of compensation for most federal civilian employees. It's a structured system with 15 grades, each representing a different level of responsibility and expertise. Within each grade are 10 steps, reflecting longevity and performance. Movement within this framework, whether through step increases or grade promotions, governs how an employee's salary progresses.
Understanding the rules surrounding GS pay progression empowers employees to anticipate their earning potential and strategize career moves. It allows them to recognize the value of performance and experience in their compensation trajectory. This knowledge is also vital for supervisors who play a role in recommending and approving these increases, ensuring fair and consistent application of the rules.
The GS pay system has evolved over time, reflecting changes in economic conditions, government priorities, and the need to attract and retain qualified employees. The current system, while structured, aims to offer competitive compensation while recognizing experience and performance. Understanding its history provides context for the current rules and potential future adjustments.
One of the most important aspects of the GS pay scale is its transparency. The publicly available pay tables, along with established rules for increases, offer predictability and accountability. This transparency fosters trust within the system and allows employees to clearly understand how their compensation is determined. It also ensures consistency in pay administration across different agencies and locations.
A step increase represents advancement within a specific grade. Typically, employees receive a step increase after serving a prescribed period at their current step. These periods vary depending on the step. For example, advancement from step 1 to step 2 might occur after one year, while progressing from step 4 to step 5 might require two years.
A grade increase, or promotion, signifies a move to a higher GS grade. This typically involves taking on a position with greater responsibilities and requiring higher-level skills. Promotions are often competitive and based on merit, performance, and meeting specific qualifications.
Benefit 1: Predictable Income Progression: The structured nature of the GS pay scale allows employees to anticipate their salary growth based on time in grade and potential promotions. For example, an employee at GS-7, Step 5 can see on the pay table what their salary will be when they reach Step 6.
Benefit 2: Performance Recognition: While step increases are generally time-based, outstanding performance can sometimes lead to accelerated step increases, providing tangible reward for exceeding expectations.
Benefit 3: Transparency and Fairness: The public availability of the GS pay tables and the clearly defined rules governing increases promote transparency and fairness within the system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of GS Pay Scale Structure
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable Salary Progression | Limited Negotiation Power |
| Transparency and Fairness | Potential Salary Compression |
| Nationwide Consistency | Difficulty Attracting Highly Specialized Talent |
Best Practices for Implementing GS Pay Increase Rules:
1. Maintain Accurate Records: Ensure accurate documentation of employee performance and time in grade to support pay increase recommendations.
2. Communicate Clearly: Openly communicate with employees about the GS pay scale, increase eligibility criteria, and performance expectations.
3. Consistent Application: Apply the rules consistently across all employees to ensure fairness and equity.
4. Regular Review: Periodically review and update internal procedures related to GS pay administration to reflect any changes in regulations.
5. Training and Development: Provide training for supervisors on proper implementation of GS pay increase rules.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How often do step increases occur? The waiting periods for step increases vary depending on the step.
2. How are grade increases determined? Grade increases are usually tied to promotions to positions with higher responsibilities and qualifications.
3. What is locality pay? Locality pay adjustments are added to the base GS salary to account for cost-of-living differences in various geographic locations.
4. How can I find the current GS pay tables? The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) website provides access to the most up-to-date GS pay tables.
5. Can performance affect my step increase? While step increases are generally time-based, exceptional performance can sometimes lead to accelerated increases.
6. What is a within-grade increase? A within-grade increase is another term for a step increase.
7. How are promotions handled within the GS system? Promotions to higher grades typically involve a competitive application process.
8. Who can I contact if I have questions about my GS pay? Your agency's human resources department is the best resource for addressing specific questions about your pay.
Tips and Tricks: Regularly review the OPM website for updates to the GS pay tables and related regulations. Maintain open communication with your supervisor regarding your career goals and performance expectations. Familiarize yourself with the specific requirements for promotion within your agency.
The GS pay scale and its grade increase rules are integral to the compensation system for federal employees. Understanding these rules is essential for career planning, financial well-being, and fostering a sense of fairness within the federal workforce. By actively engaging with the information and resources available, employees can take control of their career progression and maximize their earning potential within the GS system. This understanding not only benefits individual employees but also contributes to a more informed and engaged workforce, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of government service. Investing time in understanding the nuances of the GS pay scale is a crucial step in navigating a successful and rewarding career in federal service. It's an investment that pays dividends in both financial security and career satisfaction.
2024 Gs Pay Scale Chart Wisconsin - The Brass Coq
Gs Pay Scale Table 2024 With Locality - The Brass Coq
Federal Gs Pay Scale 2024 San Francisco - The Brass Coq
Federal Pay Raise 2024 Washington Dc - The Brass Coq