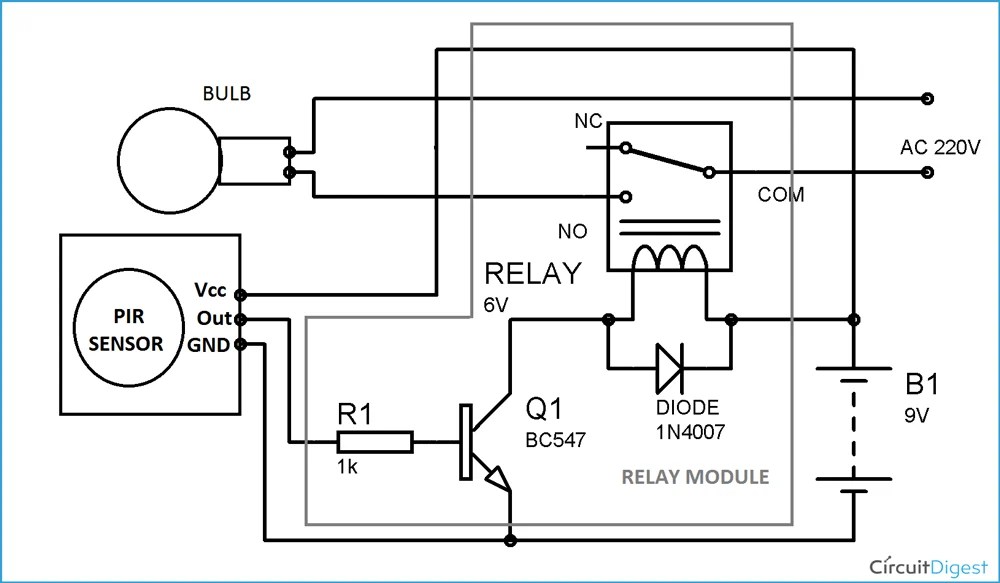
Imagine walking into a dark room and the lights turn on automatically. No fumbling for switches, just seamless, convenient illumination. This is the magic of Passive Infrared (PIR) motion sensor technology applied to automatic light control. These small, unassuming devices have revolutionized the way we interact with lighting in our homes, offices, and public spaces.
PIR sensors for automatic lighting offer a blend of convenience, security, and energy efficiency. They've become increasingly popular in recent years, transitioning from a novelty to a practical necessity in many settings. But how exactly do these sensors work their magic, and what are the key considerations for incorporating them into your own lighting systems?
At the heart of a PIR motion detector for lighting automation is a pyroelectric sensor. This sensor detects changes in infrared radiation emitted by objects within its field of view. When a warm body, such as a person or pet, moves within range, the sensor registers the change in infrared energy and triggers the connected lights. This automated response eliminates the need for manual switching, making it ideal for areas like hallways, bathrooms, and entryways.
The history of PIR sensors dates back to the 1960s, initially used in military applications. Their adoption in consumer products like automatic lighting controls gained traction in the following decades, driven by advancements in sensor technology and a growing demand for energy-saving solutions. Today, PIR sensors are integral to smart home systems and contribute significantly to building automation and energy management.
One of the primary challenges associated with PIR motion sensor lights is fine-tuning their sensitivity. False triggers caused by pets, swaying plants, or even heat sources can be frustrating. Fortunately, most modern sensors allow for adjustable sensitivity settings, enabling users to customize the sensor's responsiveness based on their specific environment and needs.
A simple example of using a PIR sensor for lighting control is installing one above your garage door. As you approach the garage, the sensor detects your presence and automatically illuminates the area, making it easier and safer to enter. Similarly, PIR sensors are highly effective in outdoor security lighting, deterring intruders while only consuming power when necessary.
Benefits of using PIR sensors for automatic light control include energy savings, enhanced security, and improved convenience. By ensuring lights are only on when needed, you significantly reduce energy consumption and lower electricity bills. The automated activation of security lights can deter potential intruders, adding an extra layer of protection to your property. And the sheer convenience of not having to manually operate light switches speaks for itself, especially in high-traffic areas.
To effectively implement PIR sensor-based lighting, consider the following action plan: identify areas where automated lighting is beneficial, choose appropriate sensor models based on range and sensitivity, ensure proper installation following manufacturer guidelines, and test and adjust sensitivity settings as needed. Successful examples include automating hallway lights, bathroom lighting, and outdoor security systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PIR Motion Sensors
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Energy Savings | False Triggers |
| Enhanced Security | Limited Range |
| Convenience | Sensitivity Issues |
Best practices for implementing PIR motion sensor lighting control include selecting the right sensor for the location, adjusting sensitivity to minimize false triggers, considering the sensor's field of view, ensuring adequate ambient light detection, and integrating sensors with smart home systems for advanced control.
Real-world examples include motion-activated hallway lights in hospitals, energy-efficient lighting in office buildings, security lighting in parking garages, automated bathroom lights in homes, and pathway illumination in gardens.
Challenges include false triggers from pets, limited detection range, susceptibility to environmental factors like temperature, and potential for malfunction. Solutions involve adjusting sensitivity, selecting appropriate sensor locations, using shielded sensors, and regular maintenance.
FAQs:
Q: How does a PIR sensor work? A: It detects changes in infrared radiation.
Q: What are the benefits of using PIR sensors for lighting? A: Energy savings, security, and convenience.
Q: Where can I use PIR sensors? A: Hallways, bathrooms, garages, outdoors.
Q: How do I adjust the sensitivity of a PIR sensor? A: Consult the manufacturer's instructions.
Q: Can PIR sensors be used with smart home systems? A: Yes, many are compatible.
Q: How much energy can I save with PIR sensors? A: Savings depend on usage but can be significant.
Q: Are PIR sensors difficult to install? A: Most are relatively easy to install with basic wiring knowledge.
Q: What is the lifespan of a PIR sensor? A: Typically several years.
Tips and tricks for PIR motion sensors include masking portions of the sensor to narrow the detection field, regularly cleaning the sensor lens, and using timers in conjunction with motion sensors for added control.
In conclusion, PIR motion sensors for automatic light control offer a powerful and practical solution for enhancing energy efficiency, improving security, and adding convenience to our daily lives. From automating simple tasks like turning on hallway lights to contributing to sophisticated building management systems, these sensors play a vital role in modern lighting design. By understanding the functionality, benefits, and best practices for implementing PIR sensors, we can harness their potential to create smarter, safer, and more sustainable living environments. Take the next step towards automating your lighting and experience the difference that PIR motion sensors can make. Investigate the options available and consider how these innovative devices can enhance your home or business.
Motion Sensor Circuit Diagram - The Brass Coq
Motion Sensor Arduino Instructables at Francis Pittman blog - The Brass Coq
Outdoor AC 220V Automatic Infrared PIR Motion Sensor Switch for LED - The Brass Coq
Outdoor AC 220V Automatic Infrared PIR Motion Sensor Switch 1pcs Motion - The Brass Coq
pir motion sensor for automatic light control - The Brass Coq
replace wall light switch with motion sensor Pir motion sensor switch - The Brass Coq
Motion Sensor Connection Diagram - The Brass Coq
Motion Sensor Light Wiring - The Brass Coq
Motion Sensor Trigger Switch at Norma Gray blog - The Brass Coq
Motion Sensor Light Switch Outdoor AC 220V Automatic Infrared PIR - The Brass Coq
Automatic Room Lights using PIR Sensor and Relay Circuit Diagram - The Brass Coq
Motion Sensor Light Switch Wiring Diagram - The Brass Coq
Smart Street Light Using Arduino Circuit Diagram - The Brass Coq
Pir Motion Sensor Led Light at Juan Marroquin blog - The Brass Coq