Ever wonder how electricity gets from the power plant to your phone? It's a journey guided by the invisible hand of circuit diagrams. These blueprints of electrical flow dictate everything from the blink of a lightbulb to the roar of a rocket engine. But what's the difference between a closed circuit diagram and its open counterpart? Prepare to unravel the electrifying mysteries!
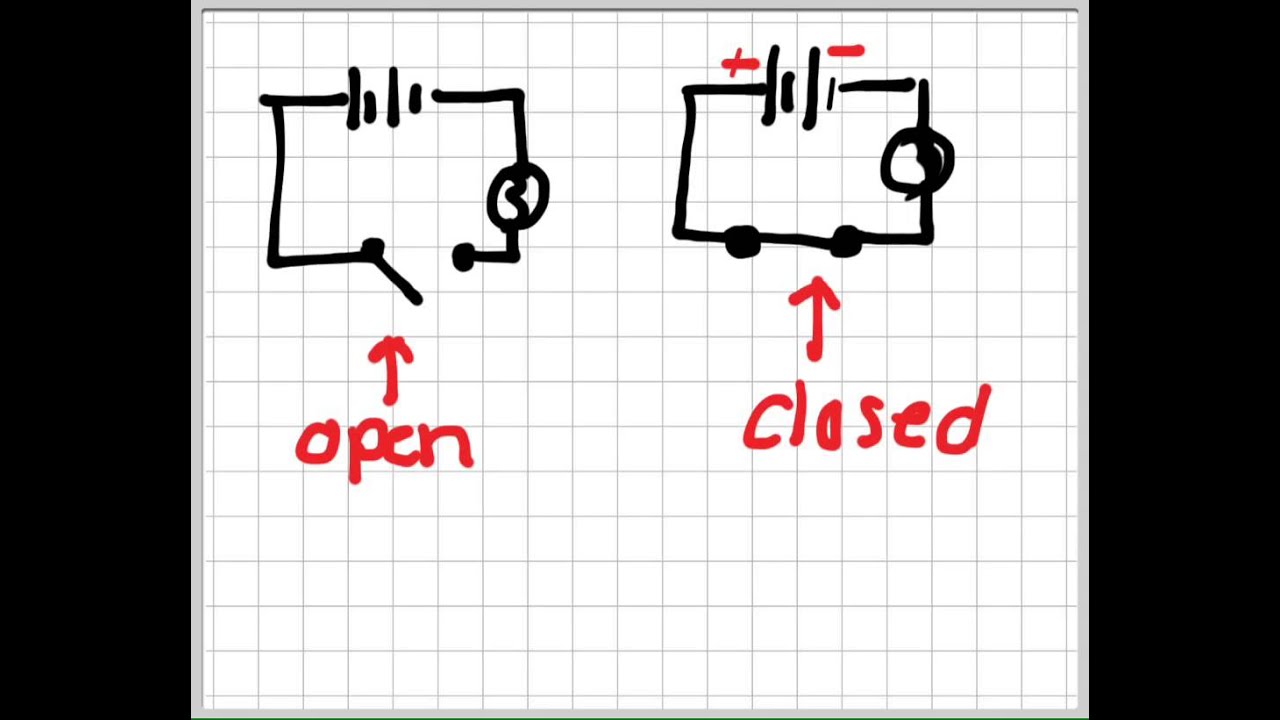
A closed circuit diagram represents a complete, unbroken pathway for electricity. Imagine it as a loop, with the power source as the starting point and all components connected in a continuous circle. Current flows freely, allowing devices to function. An open circuit diagram, on the other hand, has a break in the path, like a drawbridge stuck open. No current can flow, rendering any connected devices useless. Think of a light switch – flipping it "off" creates an open circuit.
The roots of circuit diagrams can be traced back to the early days of electrical experimentation. Pioneers like Georg Ohm and Alessandro Volta laid the groundwork for understanding electrical flow, paving the way for visual representations of circuits. These diagrams became crucial for designing and troubleshooting increasingly complex electrical systems. Without them, the modern world, with its intricate web of electronics, simply wouldn't exist.
A significant issue with closed circuits is the risk of short circuits. A short circuit occurs when the current bypasses the intended path, often due to faulty wiring or damaged components. This can lead to overheating, fire hazards, and damage to equipment. Open circuits, though generally safer, can indicate a problem, such as a broken wire or a malfunctioning switch. Identifying and fixing open circuits is essential for restoring functionality to electrical systems.
In its simplest form, a closed circuit can be represented by a battery connected to a light bulb via wires. When the switch is closed, the circuit is complete, and the bulb lights up. An open circuit example is the same setup, but with the switch open. The break in the pathway prevents current from reaching the bulb, keeping it off.
Benefits of understanding these diagrams include the ability to design, troubleshoot, and analyze electrical systems. With knowledge of closed circuits, you could design a simple lighting circuit for your home. Understanding open circuits allows you to diagnose why a lamp isn't working. Analyzing complex circuit diagrams empowers you to understand the inner workings of sophisticated electronic devices.
Want to delve deeper? Resources abound! Check out "Practical Electronics for Inventors" by Paul Scherz and Simon Monk for a comprehensive guide. Online resources like All About Circuits provide valuable tutorials and explanations.
Challenges in working with circuits include component failures, wiring issues, and complex circuit designs. Solutions include careful inspection, multimeter testing, and utilizing simulation software to analyze circuit behavior.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Closed and Open Circuits
| Circuit Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Closed | Powers devices, allows for continuous current flow. | Risk of short circuits, potential for overheating and fire hazards. |
| Open | Safe in terms of preventing current flow, acts as a safety mechanism. | Prevents devices from functioning, indicates a break in the circuit. |
FAQ: What is a closed circuit? How does an open circuit differ? What causes a short circuit? How do I test a circuit? What are the symbols used in circuit diagrams? What is the role of a resistor? What is Ohm's Law? What is the difference between AC and DC circuits?
Tips and tricks: Use a multimeter to test for continuity and voltage drops. Refer to component datasheets for specifications. Practice drawing and analyzing simple circuits before tackling complex ones.
In conclusion, understanding closed and open circuit diagrams is fundamental to navigating the electrical world. These visual representations of electrical flow empower us to design, build, and troubleshoot everything from simple household circuits to complex electronic systems. Recognizing the differences between closed and open circuits, along with their associated benefits and challenges, allows us to harness the power of electricity safely and effectively. Explore further, delve deeper, and unlock the electrifying potential that awaits. Master these principles, and you'll be well on your way to becoming a circuit wizard, wielding the power of electrons with confidence and skill. This knowledge is not just for engineers and electricians; it's a powerful tool for anyone curious about the inner workings of the modern world. So, grab a multimeter, crack open a textbook, and embark on your electrifying journey today! Don't just be a consumer of electricity – become a master of its flow.
Open And Closed Circuit Ppt Grade 5 - The Brass Coq
A Closed Circuit Diagram - The Brass Coq
To Draw The Diagram Of A Given Open Circuit - The Brass Coq
closed circuit and open circuit diagram - The Brass Coq
Diagram Of Open And Closed Circuit - The Brass Coq
closed circuit and open circuit diagram - The Brass Coq
Diagram Of Open And Closed Circuit - The Brass Coq
Closed Circuit And Open Circuit Diagram - The Brass Coq
closed circuit and open circuit diagram - The Brass Coq
Closed Circuit And Open Circuit - The Brass Coq
Open Circuit Diagram With Label - The Brass Coq
Open And Closed Circuit Diagram - The Brass Coq
Diagram Of Open And Closed Circuit - The Brass Coq
Open Circuit Diagram With Label - The Brass Coq
closed circuit and open circuit diagram - The Brass Coq