Ever wondered how alternating current behaves in a circuit with only a capacitor? The answer lies in the fascinating world of purely capacitive circuit phasor diagrams. These diagrams are essential tools for electrical engineers, providing a visual representation of the relationship between voltage and current in these unique circuits.
Imagine a circuit with just a capacitor and an AC source. Unlike resistors, capacitors don't dissipate energy. Instead, they store it in an electric field. This energy storage leads to a phase difference between the voltage across the capacitor and the current flowing through it. Phasor diagrams help us visualize this crucial difference.
The core concept behind a capacitive phasor diagram is the 90-degree phase shift. In a purely capacitive circuit, the current leads the voltage by 90 degrees. This means the current reaches its peak value a quarter-cycle before the voltage does. The phasor diagram illustrates this relationship by representing voltage and current as rotating vectors, with the current vector leading the voltage vector by 90 degrees.
Understanding this phase relationship is crucial for analyzing and designing circuits involving capacitors. Capacitors are ubiquitous in electronics, playing vital roles in everything from filtering noise to timing circuits. By understanding their behavior through phasor diagrams, we can harness their power effectively.
Historically, phasor diagrams emerged as a powerful tool for simplifying the analysis of AC circuits. Before the widespread use of complex numbers, phasor diagrams provided a graphical method to represent sinusoidal quantities and their phase relationships. They remain an invaluable tool for visualizing and understanding circuit behavior.
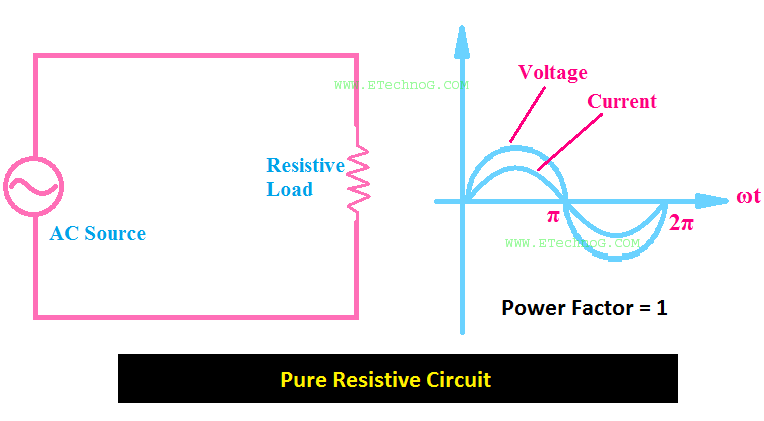
A purely capacitive circuit diagram is a simplified representation focusing solely on the capacitor's impact. Other components like resistors and inductors are absent. This simplification allows for a clearer understanding of the fundamental voltage-current relationship in a capacitive circuit.
One of the key benefits of using phasor diagrams is their ability to simplify complex calculations. They allow engineers to visualize and analyze AC circuit behavior without resorting to complicated differential equations.
Another benefit is improved circuit design. By understanding the phase relationship between voltage and current in a capacitive circuit, engineers can design more efficient and reliable circuits for various applications.
Phasor diagrams are also crucial for troubleshooting. By analyzing the phasor relationships, engineers can quickly identify potential problems and optimize circuit performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Purely Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplifies AC circuit analysis | Limited to sinusoidal waveforms |
| Visualizes phase relationships | Can be challenging for complex circuits |
| Aids in circuit design and troubleshooting | Doesn't represent transient behavior |
Best Practices for Using Phasor Diagrams:
1. Always ensure the frequency is constant.
2. Clearly label voltage and current phasors.
3. Maintain a consistent scale for the phasors.
4. Indicate the phase angle accurately.
5. Use appropriate software or tools for drawing accurate diagrams.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? A phasor is a rotating vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.
2. Why does current lead voltage in a capacitor? Due to the capacitor's charging and discharging behavior.
3. What is the impedance of a capacitor? It's the opposition to AC current flow.
4. How is reactance different from resistance? Reactance is frequency-dependent.
5. What are the applications of capacitive circuits? Filtering, energy storage, power factor correction.
6. How do you draw a phasor diagram? Represent voltage and current as vectors with appropriate phase difference.
7. Why are phasor diagrams important? They simplify AC circuit analysis.
8. What are the limitations of phasor diagrams? They are primarily for steady-state analysis.
Tips and Tricks: Using software tools can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency when working with phasor diagrams.
In conclusion, purely capacitive circuit phasor diagrams are indispensable tools for anyone working with AC circuits. They provide a clear and concise way to visualize the relationship between voltage and current, simplifying complex analyses and facilitating efficient circuit design. By mastering these diagrams, engineers can harness the full potential of capacitors in a wide range of electronic applications. Understanding these diagrams empowers engineers to tackle complex circuit challenges effectively, opening doors to innovation and efficient design. Exploring this fundamental concept is key to building a strong foundation in electrical engineering and its countless applications. From power systems to electronics, a thorough grasp of capacitive circuit behavior is crucial. So, dive in, explore, and unlock the power of phasor diagrams!
Purely Resistive Circuit Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
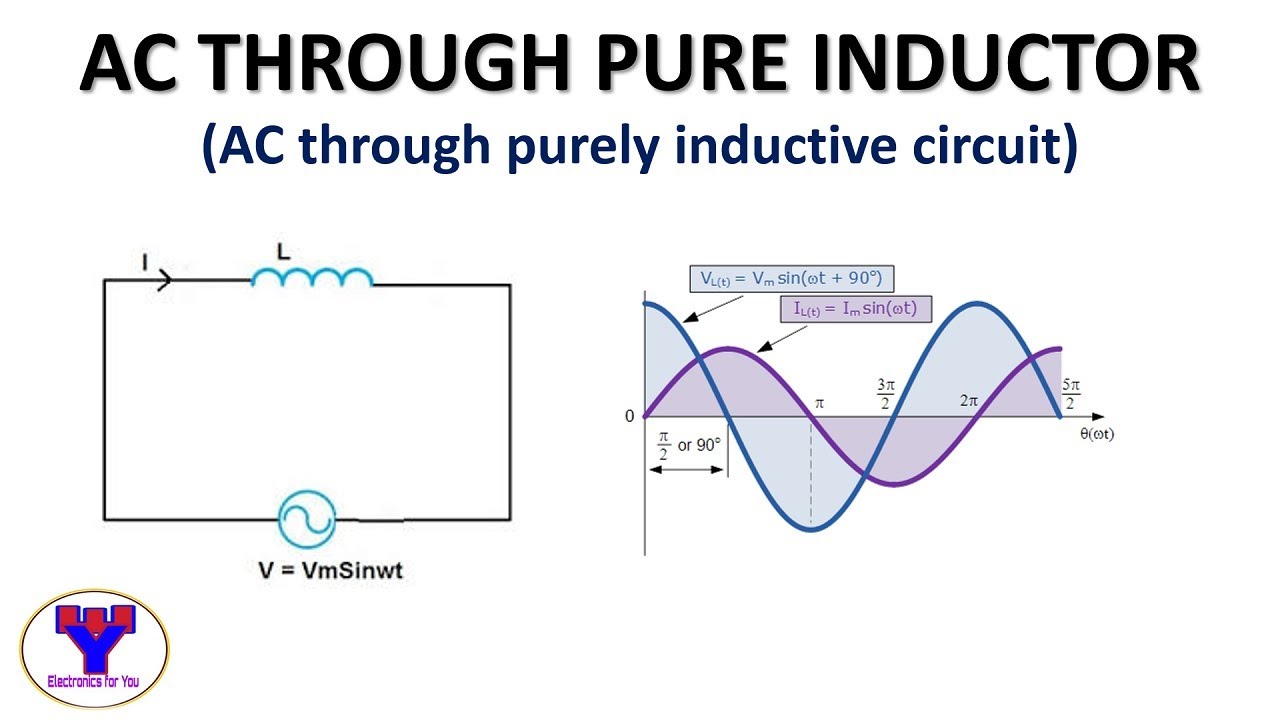
Phasor Diagram For Inductive Circuit - The Brass Coq
SOLVED Design the circuit and sketch the waveform and the phasor - The Brass Coq
What is a Purely Inductive Circuit Circuit Diagram Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
Purely Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
Purely Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
Phasor Diagram For Capacitive Circuit - The Brass Coq
Purely Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
What is a Power Triangle Active Reactive Apparent Power - The Brass Coq
Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
What is a Purely Inductive Circuit Circuit Diagram Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
Purely Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
Purely Capacitive Circuit Phasor Diagram - The Brass Coq
ANSWERED The phasor diagram shown below represents cot Purely - The Brass Coq
The Current In An Inductive Circuit - The Brass Coq