Ever wondered how businesses keep track of their financial transactions with pinpoint accuracy? The secret lies in a fundamental accounting principle: double-entry bookkeeping, which revolves around the concept of debits and credits. This system forms the backbone of modern accounting, providing a robust and reliable method for recording and analyzing financial data.
Debits and credits, often represented as "Debe" (debit) and "Haber" (credit) in Spanish accounting terminology, aren't simply about increases and decreases. They represent a dynamic relationship within the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity). Every transaction affects at least two accounts, ensuring the equation remains balanced, and providing a complete picture of financial activity.
Understanding the interplay between debits and credits is essential for anyone involved in financial management, from small business owners to seasoned financial analysts. This knowledge empowers you to interpret financial statements, make informed business decisions, and maintain accurate financial records. Without a solid grasp of these fundamentals, navigating the financial landscape can feel like traversing a minefield.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of debits and credits, exploring their history, mechanics, and practical applications. We'll demystify this seemingly complex concept, providing clear explanations and real-world examples to help you build a solid foundation in accounting principles.
The double-entry bookkeeping system, rooted in 15th-century Italy, revolutionized financial record-keeping. Luca Pacioli, a Franciscan friar and mathematician, is credited with formalizing this system, which has remained largely unchanged for centuries. Its enduring relevance speaks volumes about its effectiveness and adaptability in tracking financial transactions across diverse industries and economic landscapes.
Debits increase asset, expense, and dividend accounts, while they decrease liability, owner's equity, and revenue accounts. Credits, conversely, increase liability, owner's equity, and revenue accounts, and decrease asset, expense, and dividend accounts. This seemingly counterintuitive relationship is crucial to maintaining the balance of the accounting equation.
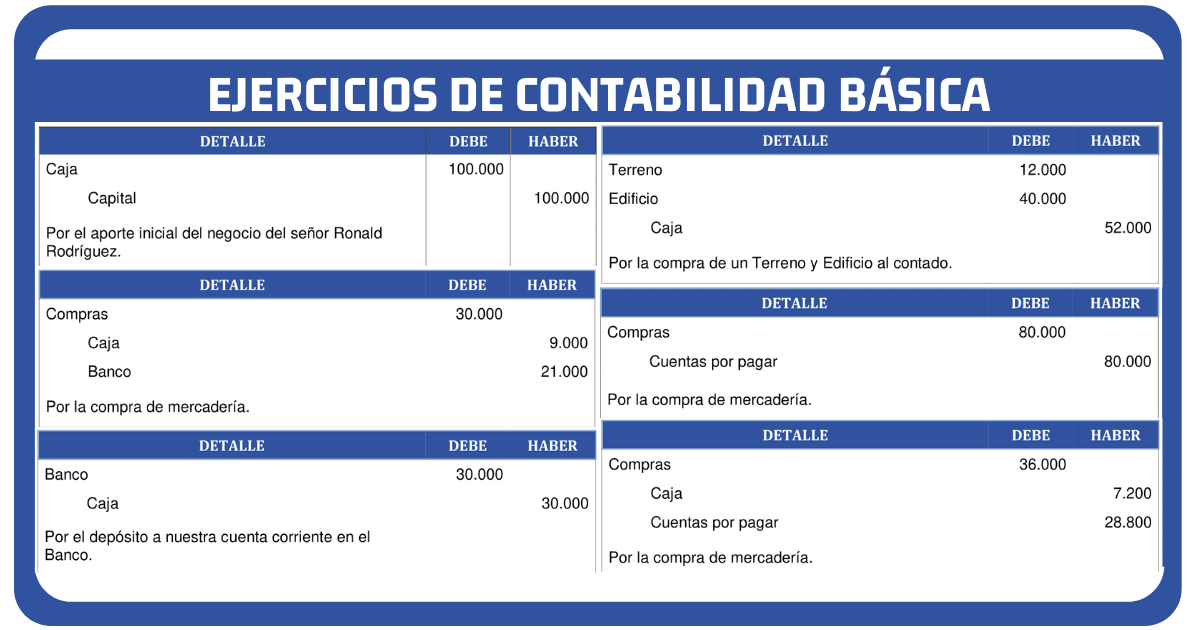
For example, if a company purchases equipment for $1,000 in cash, the equipment (asset) account is debited by $1,000, and the cash (asset) account is credited by $1,000. Notice how the accounting equation remains balanced: the increase in one asset is offset by the decrease in another.
Benefits of using double-entry bookkeeping include improved accuracy, fraud prevention, and better financial analysis. The dual entry system ensures checks and balances, making errors more readily apparent. The comprehensive record of transactions facilitates detailed analysis of financial performance and aids in informed decision-making.
One best practice is to meticulously document every transaction with supporting documentation, like invoices or receipts. This ensures auditability and helps prevent errors. Regularly reconciling bank statements with accounting records is another essential practice for identifying discrepancies and maintaining accurate financial reporting. Consistently applying accounting principles and seeking professional guidance when needed are also crucial for effective financial management.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Double-Entry Bookkeeping
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved Accuracy | More Complex than Single-Entry |
| Better Fraud Detection | Requires More Time and Resources |
| Enhanced Financial Analysis | Can be Challenging for Non-Accountants |
Challenges in implementing double-entry bookkeeping can include the initial learning curve, the need for consistent data entry, and the potential for software compatibility issues. However, these challenges can be overcome through proper training, dedicated resources, and careful software selection.
FAQ: What is a debit? What is a credit? What is the accounting equation? How does double-entry bookkeeping work? Why is double-entry bookkeeping important? What are some common accounting errors? How can I improve my accounting skills?
Tips for success include staying organized, using accounting software, and seeking professional help when needed.
In conclusion, understanding the principles of debits and credits, the foundation of double-entry bookkeeping, is paramount for sound financial management. From ensuring accuracy to facilitating informed decision-making, mastering this fundamental accounting concept empowers businesses and individuals to navigate the financial landscape with confidence. By embracing best practices, consistently applying these principles, and leveraging available resources, you can unlock the full potential of double-entry bookkeeping and achieve financial clarity. This knowledge not only strengthens your financial foundation but also provides a competitive edge in today's complex business environment. Take the time to understand and apply these principles, and you'll be well-equipped to manage your finances effectively and achieve your financial goals. Continuous learning and staying updated with accounting best practices are crucial for long-term success in this dynamic field.
Degré Celsius Est en train de pleurer En permanence asientos contables - The Brass Coq
Debe y haber fundamentos de contabilidad - The Brass Coq
BLOG CONTABLE GUIA PARA REALIZAR ASIENTOS CONTABLES - The Brass Coq
luz de sol Marcar Frank Worthley plantilla excel debe haber y saldo - The Brass Coq
Ejemplos de Debe y Haber en Contabilidad Guía Completa para Entender - The Brass Coq
Que Es Debe Y Haber Ejemplos Coleccion De Ejemplo Images - The Brass Coq
INTRODUCCIÓN AL DEBE Y EL HABER EN COMPRAS - The Brass Coq
Debe y Haber en Contabilidad Diferencia - The Brass Coq
debe y haber en contabilidad ejemplos - The Brass Coq
ᐈ Debe y Haber en Contabilidad - The Brass Coq
Qué es el Debe - The Brass Coq
debe y haber en contabilidad ejemplos - The Brass Coq
Qué es el Debe y el Haber en Contabilidad - The Brass Coq
Debe y haber fundamentos de contabilidad - The Brass Coq
Debe y Haber en Contabilidad - The Brass Coq