Ever glanced at your fuel gauge, only to be met with a confusing reading? Perhaps it’s stuck on full, perpetually on empty, or bouncing erratically. A faulty fuel gauge can lead to unexpected stops, inconvenient refueling detours, and even damage to your vehicle. Understanding how to diagnose and fix these issues is an essential skill for any driver.
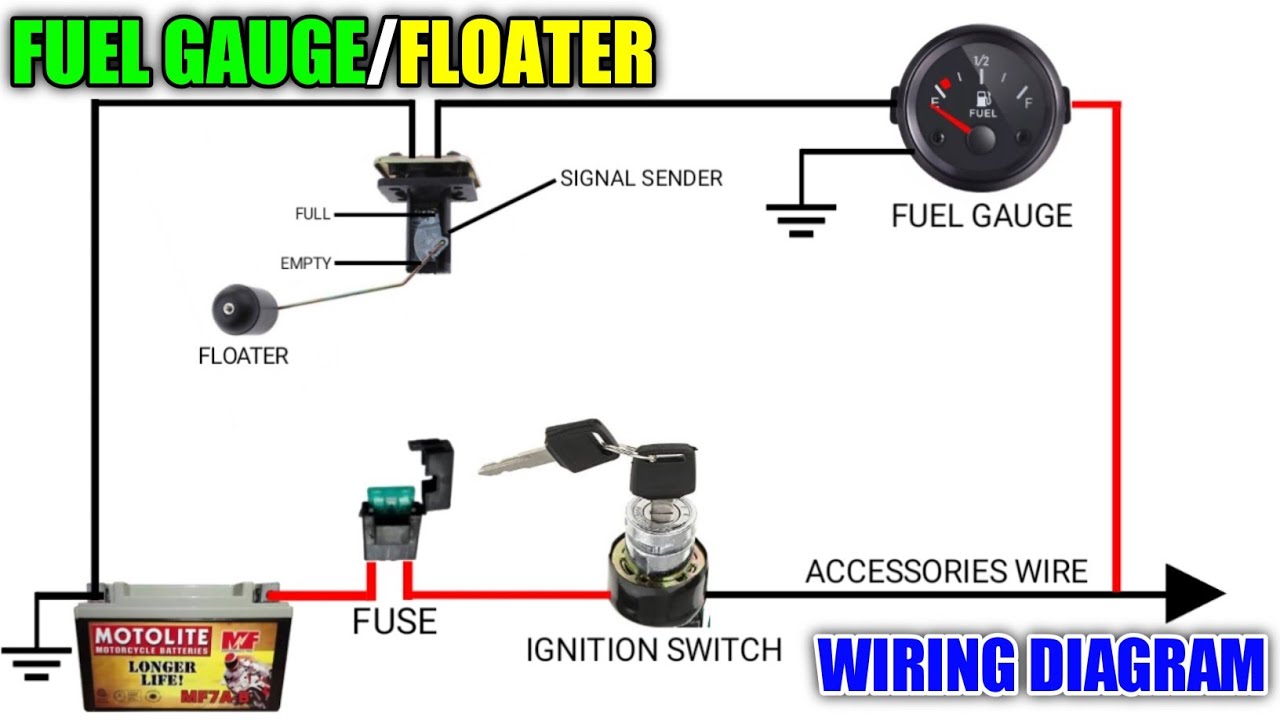
The fuel gauge system is more than just a needle and a dial; it’s a critical communication link between your fuel tank and your dashboard. This system, comprised primarily of the fuel gauge and the sending unit, provides you with vital information about how much fuel remains in your tank, enabling you to plan your journeys and avoid running dry. Troubleshooting this system requires a systematic approach, but the rewards – a reliably accurate fuel gauge – are well worth the effort.
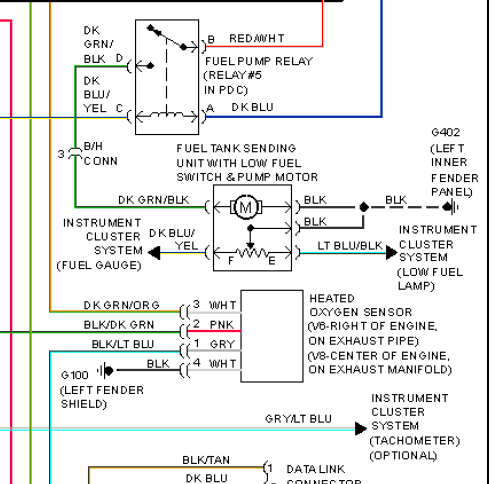
The development of the fuel gauge system mirrors the evolution of the automobile itself. Early vehicles relied on simple sight gauges, requiring drivers to physically check the fuel level in the tank. As cars became more sophisticated, so did their fuel systems, introducing float-based sending units and electrically driven gauges. Troubleshooting these newer systems often involves checking electrical connections, the sending unit’s float, and the gauge itself.
The primary role of diagnosing fuel sending unit and gauge issues is to ensure accurate fuel level readings. Inaccurate readings can lead to a range of problems, from the inconvenience of unexpected fuel stops to potential damage to the fuel pump if the vehicle runs completely dry. Being able to pinpoint the source of the problem, whether it’s a faulty sending unit, a malfunctioning gauge, or a wiring issue, allows for a targeted and effective repair.
Common issues encountered when diagnosing fuel sender and gauge problems include a stuck or erratic fuel gauge, a gauge that reads full or empty all the time, and rapid fluctuations in the fuel level reading. These problems can stem from a variety of causes, including a faulty sending unit float, a damaged wiring harness, or a malfunctioning fuel gauge. Understanding these common issues and their potential causes is the first step towards accurate troubleshooting.
The sending unit, typically located inside the fuel tank, houses a float arm connected to a variable resistor. As the fuel level changes, the float moves, altering the resistance and sending a corresponding signal to the fuel gauge. A common issue is a binding or sticking float arm, preventing accurate readings. For example, if the float arm gets stuck in the up position, the gauge might constantly read full, even if the tank is nearly empty.
Three key benefits of troubleshooting your fuel gauge system are: avoiding running out of fuel, which can lead to dangerous situations, especially in remote areas; preventing damage to your fuel pump, which can be costly to replace; and ensuring accurate fuel economy calculations, allowing you to track your vehicle's performance and identify potential issues early on.
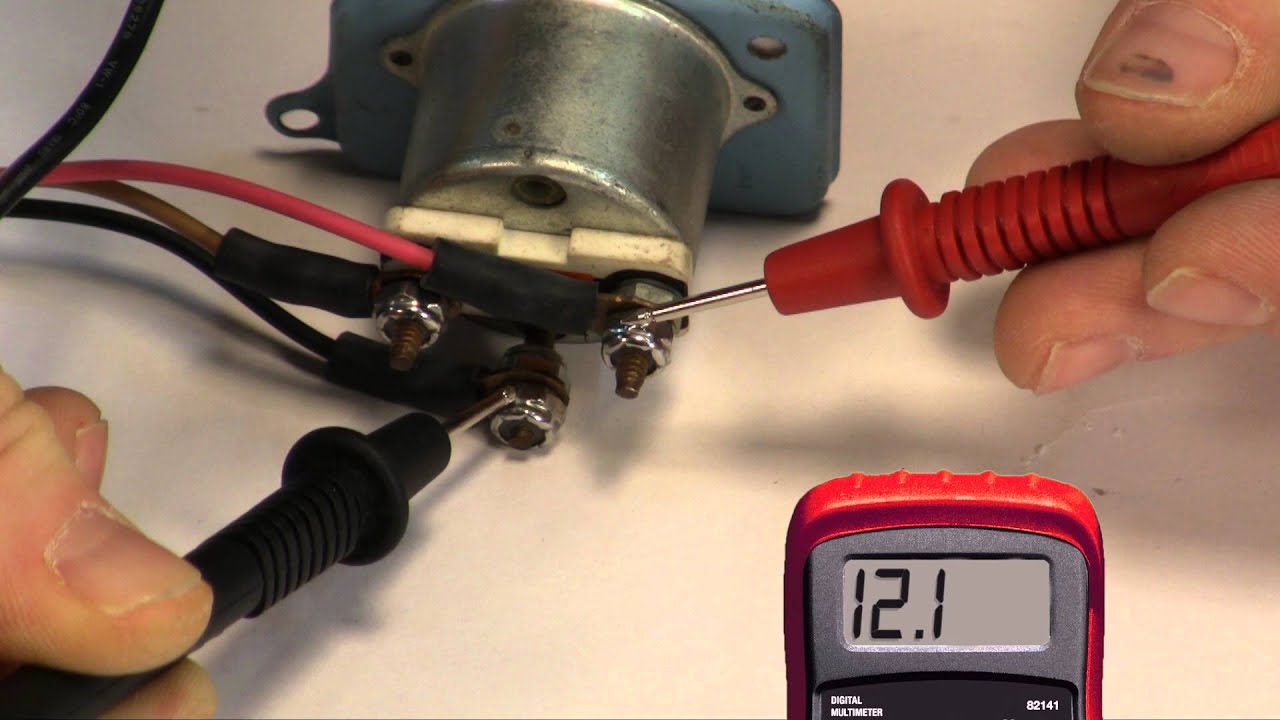
Troubleshooting fuel gauge problems begins with checking the fuse. Then, check the wiring connections at both the sending unit and the fuel gauge. Using a multimeter, test the resistance of the sending unit. If the resistance doesn’t change as the float arm is moved, the sending unit is likely faulty. If the sending unit tests correctly, the problem may lie with the gauge itself.
Troubleshooting Checklist:
1. Check the fuel gauge fuse.
2. Inspect the wiring harness for damage.
3. Test the sending unit's resistance.
4. Check the fuel gauge for proper operation.
Step-by-step Guide for Testing the Sending Unit:
1. Disconnect the wiring connector from the sending unit.
2. Connect the multimeter leads to the sending unit terminals.
3. Move the float arm through its full range of motion.
4. Observe the resistance readings on the multimeter. The resistance should change smoothly as the float arm moves.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DIY Troubleshooting
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Cost savings | Potential for misdiagnosis |
| Increased knowledge of your vehicle | Risk of causing further damage |
Five Best Practices: 1. Always disconnect the battery’s negative terminal before working on the fuel system. 2. Use the correct tools and safety equipment. 3. Consult a repair manual specific to your vehicle. 4. If you're unsure, seek professional help. 5. Regularly check your fuel gauge for accuracy.
Five Real Examples: 1. A fluctuating gauge was caused by a loose wire. 2. A gauge stuck on empty was due to a faulty ground connection. 3. A gauge reading full constantly had a stuck float arm. 4. Erratic readings were traced back to a damaged sending unit. 5. A completely dead gauge resulted from a blown fuse.
Five Challenges and Solutions: 1. Difficulty accessing the sending unit – Solution: Consult a repair manual for instructions. 2. Damaged fuel lines – Solution: Replace the damaged lines. 3. Corroded connectors – Solution: Clean or replace the connectors. 4. Incorrect multimeter readings – Solution: Check the multimeter’s connections and battery. 5. Persistent issues despite troubleshooting - Solution: Consult a professional mechanic.
FAQs: 1. Why is my fuel gauge inaccurate? Answer: Several factors can cause this, from a faulty sending unit to wiring issues. 2. How often should I check my fuel gauge? Answer: It's a good practice to monitor it regularly while driving. 3. Can I drive with a broken fuel gauge? Answer: Yes, but it's risky and not recommended. 4. How much does it cost to replace a sending unit? Answer: Costs vary depending on the vehicle. 5. How long does it take to replace a sending unit? Answer: This depends on the vehicle's make and model. 6. What tools do I need to troubleshoot a fuel gauge? Answer: A multimeter, screwdrivers, and possibly a fuel pressure tester. 7. Where is the sending unit located? Answer: Typically inside the fuel tank. 8. Can I fix a fuel gauge problem myself? Answer: Basic troubleshooting is possible, but complex issues may require professional assistance.
Tips and Tricks: When testing the sending unit, gently move the float arm. Forceful movements can damage the unit. Also, always use a repair manual specific to your vehicle. Wiring diagrams and procedures can vary greatly between makes and models.
A properly functioning fuel gauge isn't just a convenience; it's a crucial component of your vehicle's safe and efficient operation. Ignoring fuel gauge problems can lead to inconvenient breakdowns, costly repairs, and even potentially dangerous situations. By understanding the basic principles of fuel gauge and sending unit troubleshooting, you can avoid these pitfalls and keep your vehicle running smoothly. Taking proactive steps to diagnose and address fuel gauge issues not only saves you money and hassle but also empowers you to maintain your vehicle's reliability. Don't wait for your fuel gauge to fail; take the time to understand its operation and learn the basic troubleshooting steps. Your wallet and your peace of mind will thank you.
Fuel Gauge Wiring Diagram Boat - The Brass Coq
How To Troubleshoot Your Marine Fuel Level Sender - The Brass Coq
Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Wiring Diagram - The Brass Coq
3 Wire Fuel Sending Unit Wiring Diagram - The Brass Coq
Universal Electric Sending Unit For Gasoline Camping World 54 OFF - The Brass Coq
2006 Dodge Ram 1500 Fuel Pump Wiring Diagram - The Brass Coq
Gm Fuel Gauge Wiring Diagram - The Brass Coq
Fuel Gauge Schematic Diagram - The Brass Coq
troubleshooting fuel gauge and sending unit - The Brass Coq
Buy 100TECH Fuel Gauge Sending Unit High Resolution 5130mm SUS316 - The Brass Coq
Hooking Up A Fuel Gauge at Terrance Brown blog - The Brass Coq
Buy Boat Fuel Sending Unit 240 - The Brass Coq
Fuel Gauge Wiring Diagram Chevy - The Brass Coq
Jeep Cj7 Fuel Gauge Wiring Diagram - The Brass Coq
Troubleshooting Marine Fuel Gauge And Sender - The Brass Coq